First Battle of St Albans
| First Battle of St Albans | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Wars of the Roses | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| House of York | House of Lancaster | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 3,000–7,000[2] | 2,000[3] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 60[3] | 100[1] | ||||||
The First Battle of St Albans took place on 22 May, 1455, at St Albans, 22 miles (35 km) north of London, and traditionally marks the beginning of the Wars of the Roses in England.[4] Richard, Duke of York, and his allies, the Neville Earls of Salisbury and Warwick, defeated a royal army commanded by Edmund Beaufort, Duke of Somerset. Unusually, the battle was contested in the town of St Albans itself, with the bulk of the fighting taking place in the streets and a tavern being used as a redoubt. Somerset was killed in the battle, and King Henry VI captured, clearing the way for a subsequent parliament to appoint Richard of York Lord Protector.[5]
Background
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2017) |
The incapacitation of Henry VI by mental illness[6] in 1454 led to the recall to court of Richard of York, his closest adult relative. In 1447, York had been appointed Lieutenant of Ireland, and had essentially been in exile from England. His long-time rival, Edmund Beaufort, Duke of Somerset, the favourite of the king, had been given the Lieutenancy of France. After Somerset's failure in France, York unexpectedly returned to London with significant support not only from the nobility, most of whom saw the incompetence of Somerset's efforts in France, but also from the public. He presented himself as a champion of the law and urged the king to have Somerset tried and held accountable for his failures. He also wished to be recognised as heir presumptive to the English throne while Henry VI was childless.
York formed an army to force the issue in 1452, and after meeting with the council of war and the king, who desperately wanted to avoid a conflict, York's demands were agreed to. York disbanded his army as a result, but was soon arrested and held prisoner for three months. An execution was avoided, as the king was nervous about arousing trouble; the Duke of York was very popular and known as a man of honour. York was released only after he had agreed to swear an oath at St Paul's Cathedral that he would never again take up arms against the king.
After the English army, led by Sir John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, was routed in the Battle of Castillon, Henry VI suffered a complete mental breakdown and was unable to perform his royal duties. Somerset had attempted to take control of the country and sought to make himself Lord Protector. However, Somerset underestimated the Duke of York's influence and popularity, as many nobles on the council (including York's closest allies, his brother-in-law Richard Neville, Earl of Salisbury and Salisbury's son Richard, Earl of Warwick) were on York's side. Thus, York was given the appointment to govern England as Lord Protector and First Councillor of the realm while the king remained unfit. He used that position to move against his chief rival, express the bitterness which had accumulated over the years, and have the Duke of Somerset imprisoned. During those 14 months, both sides of the conflict were forming. There was also conflict between the Dukes of York and Somerset, members of the two richest and most prominent families of the north, and the Percys and Nevilles, who were having their own conflicts. The Percys were Earls of Northumberland; the Nevilles possessed both Salisbury and Warwick (received through the right of their wives), and they were one of the richest families in all England. The Nevilles were also related to the Duke of York by marriage, as the Duchess of York was Cecily Neville, the sister of the Earl of Salisbury. Much of the fighting was over land and money. Both families were clearly choosing sides, the Percys for Somerset and the Nevilles for York.[7]
By Christmas 1454, King Henry had recovered from his illness, which removed the basis for York's authority.[8] Somerset was released and restored to his former position of power. Having reconvened the court at Westminster by mid-April 1455, Henry and a select council of nobles decided to hold a great council at Leicester. York and his closest allies anticipated that Somerset would bring charges against them at the assembly. They gathered an armed retinue and marched to stop the royal party from reaching Leicester by intercepting it at St Albans.
Prelude
[edit]On 18 May, news reached the king and the Duke of Somerset in London that York and his allies had raised a retinue and were marching south to London down the Great North Road. On Somerset's instructions, Cardinal Thomas Bourchier wrote to them to order them to disband. The Duke of York and the Earls of Warwick and Salisbury authored a letter at Royston on 20 May to insist that they were loyal to the king and had only brought their forces as protection from their enemies. Whether York intended to march on London or capture the king on the road to Leicester is unknown, but Somerset called his allies to St Albans and left London on 21 May, likely for fear of the pro-Yorkist London. Marching to St Albans with their own retainers, the Yorkists wrote a letter directly to the king on 21 May from Ware, where they turned off the Great North Road and began the approach to St Albans. On the night of 21 May, the king and Somerset were at Watford while the Yorkists were camped on the road between Ware and St Albans.[9]
Battle
[edit]
The Lancastrian army of 2,000 troops arrived at St Albans first, with Humphrey Stafford, Duke of Buckingham, in command,[10] and proceeded to defend it[11] by placing troops along the Tonman Ditch and at the bars in Sopwell Lane and Shropshire Lane. The reassignment of Buckingham from Somerset as commander of the army had been a last-minute decision by Henry VI, whether from fear of Somerset's past failures or of animosity towards the Duke of York. The 7,000-strong Yorkist army arrived and camped in Keyfield to the east. Lengthy negotiations ensued, with heralds moving back and forth between the rival commanders.[12] After a few hours, it was believed in the Yorkist camp that King Henry VI knew nothing of the letters of negotiation.[3]
The Duke of York had made his intentions clear and wanted Somerset punished, then executed. In a message to Henry VI, he stated:
... surrender to us such as we will accuse, and not to resist til we have him which deserves death.[7]
Demanding so much from the king and setting the rules was a dangerous move by York. The very act of displaying such an aggressive front to the king was treasonous, but his popularity kept York confident and supported. In a fit of uncharacteristic regency, Henry refused, replying,
By the faith that I owe to St. Edward and the crown of England I shall destroy every mother's son and they shall be hanged, and drawn and quartered.[7]
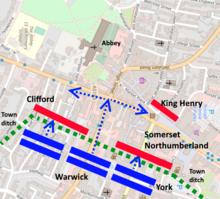
After several hours, Richard, despairing of a peaceful solution, decided to attack. Although his army may have been unwilling to attack King Henry, the Royal Standard was not visible[13] and may even have been negligently propped against a wall by the royal standard-bearer, the Earl of Wiltshire.[14] Most of Henry's forces were surprised by the suddenness of Richard's attack, and most of the army was expecting a peaceful resolution similar to that which occurred at Blackheath in 1452. However, two Yorkist frontal assaults down the narrow streets against the barricades near St Peter's Church, which were commanded by Lord Clifford,[15] made no headway and resulted in heavy casualties for the Yorkists.[1]
Warwick led a reserve force into an unguarded part of the town, through back lanes and gardens. Soon after, he appeared in the market square, where the main body of Henry's troops were talking and resting. Henry's troops did not yet expect to be involved in the fighting, as many were not even wearing their helmets. Warwick charged instantly with his forces and routed the Lancastrians.[16]
Somerset, knowing very well that York would never let him live, sought refuge at the Castle Inn. When the Yorkists surrounded the building, Somerset tried to fight his way out. He charged onto the main street, over the bodies of the defenders, and killed four men before he was struck down. The Earl of Northumberland was killed trying to get to the refuge at the Castle Inn. Lord Clifford of Skipton, an ally of Percy, was hacked to death in the main street. On Warwick's orders, his archers then shot at the men surrounding the king, killing several and injuring the king and the Duke of Buckingham.[1]
The Lancastrians still manning the barricades and fighting against York's and Salisbury's men realised the Yorkists had outflanked them and, fearing an attack from behind, abandoned their positions and fled the town. Overall, the battle did not last longer than half an hour, and was decided by Warwick charging into the town when the Lancastrians were unprepared.
Aftermath
[edit]At the First Battle of St Albans, fewer than sixty were killed of approximately 5,000 combatants,[17] but politically, it was a complete victory for York and the Nevilles. York had captured the king and restored himself to absolute power, and Somerset and the Nevilles' northern rivals Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland, and Lord Clifford fell during the rout.[1] Among the wounded were Buckingham; Thomas de Courtenay, Earl of Devon; Jasper Tudor (half-brother of the king); and Somerset's son Henry Beaufort, Earl of Dorset.[18] The sudden attack by, and bravery of, the 26-year-old Earl of Warwick began to establish his famous military career and his reputation as "the kingmaker".
The next day, York escorted King Henry back to London and was appointed as Protector of England by the Parliament a few months later.[5]
In literature
[edit]
Shakespeare's historic play Henry VI, Part 2 ends with the conclusion of the battle.
Trinity (known in the US as Margaret of Anjou), the second book of the Wars of the Roses series by Conn Iggulden, dramatises the battle as a moment of indecision for Richard of York but as a powerful victory for the Neville faction during the Percy–Neville feud.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Goodman 1981, p. 24.
- ^ Griffiths 1981, p. 742.
- ^ a b c Griffiths 1981, p. 744.
- ^ Davies 2000, p. 147.
- ^ a b Hicks 2010, p. 114.
- ^ Bark, N. (2002). "Did schizophrenia change the course of English history? The mental illness of Henry VI". Medical Hypotheses. 59 (4): 416–421. doi:10.1016/s0306-9877(02)00145-7. PMID 12208181.
- ^ a b c Haigh, Philip A. (1995). The Military Campaigns of the Wars of the Roses. Surrey: Bramley Books. pp. 3–7. ISBN 978-1-85833-770-8.
- ^ Hicks 2010, p. 107.
- ^ The Battles of St Albans (Battleground War of the Roses). pp. 45–46.[full citation needed]
- ^ Hicks 2010, p. 108.
- ^ Goodman 1981, p. 22.
- ^ Bertram Percy Wolffe, Henry VI, (St. Edmundsbury Press, 2001), 292.
- ^ Sadler 2011, p. 7.
- ^ Sadler 2011, p. 9.
- ^ Griffiths 1981, p. 745.
- ^ Hicks 2003, p. 35.
- ^ Jones 2015, p. 149.
- ^ Hicks 2010, p. 110.
References
[edit]- Davies, C.S.L. (2000). "Government and Politics in England: problems of succession". In Haigh, Christopher (ed.). The Cambridge Historical Encyclopedia of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press.
- Goodman, Anthony (1981). The Wars of the Roses: Military Activity and English Society, 1452–97. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. ISBN 978-0-7100-0728-5.
- Griffiths, R.A. (1981). The Reign of King Henry VI. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04372-5.
- Hicks, Michael (2003). The Wars of the Roses 1455–1485 (PDF). Essential Histories. Vol. 54. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-491-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2013.
- Hicks, Michael (2010). The Wars of the Roses. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11423-2.
- Jones, Dan (2015). The Hollow Crown: The Wars Of The Roses And The Rise Of The Tudors. Faber & Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-28808-3.
- Sadler, John (2011). Towton: The Battle of Palm Sunday Field 1461. Pen & Sword Military. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-84415-965-9.
- Wolffe, Bertram Percy (2001). Henry VI. St. Edmundsbury Press.
Further reading
[edit]- Burley, Elliott & Watson, The Battles of St Albans, Pen & Sword, 2007, ISBN 978-1-84415-569-9



